Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders Case
She reports noticing a small bump in the midline of her neck for the past several weeks that seems to have gotten significantly larger in the past several days. Physical exam is notable for bilateral anterior cervical lymphadenopathy and a nontender, 2 cm right-sided thyroid nodule. You notice that her voice sounds rather hoarse. Given the history and physical exam, you are concerned that she may have thyroid cancer.
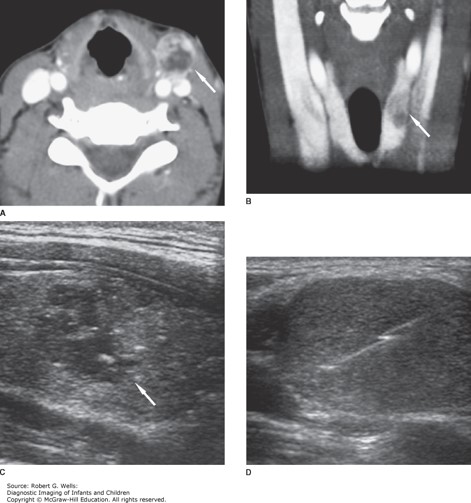
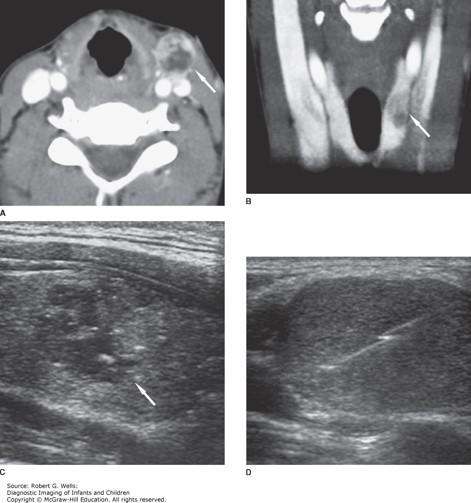
Differentiated thyroid carcinoma (papillary). This 14-year-old girl presented with a palbable left neck mass. A. Axial contrast-enhanced CT at the level of the mass shows an enlarged, heterogeneously enhancing lymph node (arrow). B. The primary tumor is visible on this coronal image as a hypoattenuating lesion (arrow) in the left lobe of the thyroid. C. The nodule (arrow) is predominantly hypoechoic on this longitudinal sonographic image. D. Percutaneous core needle biopsy of the metastatic lymph node provided material for a histological diagnosis.
All of the following are clinical features that may be associated with thyroid carcinoma EXCEPT:
A. History of external radiation to the head or neck, or both.
B. History of exposure to nuclear fallout.
C. Bradycardia.
D. Dysphagia.
E. Vocal cord paralysis.
The correct is C.
The correct answer is “C.” The most common presentation of a patient with thyroid cancer is the presence of a solitary thyroid nodule or mass. Although approximately 2% of children have palpable thyroid nodules, most of these are benign adenomas or cystic lesions. Patients with thyroid cancer may have a history of external radiation to the head and neck, exposure to nuclear fallout, a history of rapid growth of the thyroid nodule, a firm or fixed neck mass, hoarseness, dysphagia, or cervical lymphadenopathy. Thyroid cancer is divided into four main types: papillary, follicular, medullary, and anaplastic. In children, the vast majority of masses are differentiated thyroid cancer, which includes both papillary and follicular thyroid carcinomas. Medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) is notable due to the production of calcitonin from the parafollicular or C cells of the thyroid gland, and it may be associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A (MEN 2A) or MEN 2B. Diagnosis of thyroid carcinoma is made by fine needle aspiration biopsy.
Sources:
Question & Explanation: Peterson AR, Wood KE. Pediatrics Examination and Board Review. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education; 2017.
Photo: Wells RG. Diagnostic Imaging of Infants and Children; 2015.




Create a Free MyAccess Profile
AccessMedicine Network is the place to keep up on new releases for the Access products, get short form didactic content, read up on practice impacting highlights, and watch video featuring authors of your favorite books in medicine. Create a MyAccess profile and follow our contributors to stay informed via email updates.