Pediatric Gastroenterology Case
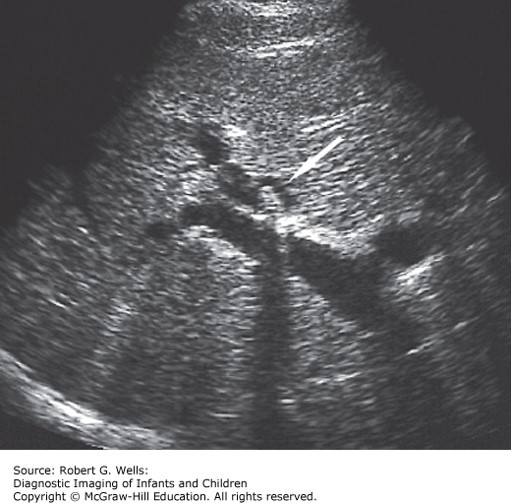
She had one episode of nonbloody, nonbilious emesis and is nauseated. She has no fever or diarrhea. On exam, she is afebrile, obese, and uncomfortable. She has tenderness in the right upper quadrant. Her direct bilirubin, GGT, and transaminase levels are elevated.
Of the list below, the most likely diagnosis is:
A. Gastroenteritis.
B. Choledocholithiasis.
C. Splenic rupture.
D. Pancreatitis.
The correct answer is “B.” Choledocholithiasis refers to gallstones in the common bile duct. Pain, or “biliary colic,” arises when a stone temporarily obstructs the biliary tree. Children and adolescents present with right upper quadrant pain, vomiting, and sometimes jaundice. The stone should be removed surgically. Stone removal by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is becoming more common.
Sources:
Question & Explanation: Peterson AR, Wood KE. Pediatrics Examination and Board Review. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education; 2017.
Photo: Wells RG. Diagnostic Imaging of Infants and Children; 2015.




Create a Free MyAccess Profile
AccessMedicine Network is the place to keep up on new releases for the Access products, get short form didactic content, read up on practice impacting highlights, and watch video featuring authors of your favorite books in medicine. Create a MyAccess profile and follow our contributors to stay informed via email updates.